IoT in ERP: Optimizing Production and Logistics Processes is revolutionizing industrial operations. The seamless integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems unlocks unprecedented efficiency gains in manufacturing and supply chain management. This powerful combination allows for real-time data collection, analysis, and automated responses, leading to significant improvements in production output, inventory control, and overall operational effectiveness.
This exploration delves into the practical applications, benefits, and challenges associated with implementing this transformative technology.
From predictive maintenance that minimizes downtime to proactive inventory management that prevents stockouts, IoT in ERP offers a comprehensive solution for optimizing processes across the entire value chain. This detailed examination will cover various aspects, including data security, technological advancements, and real-world case studies illustrating the tangible benefits achieved by companies already leveraging this innovative approach.
Introduction to IoT in ERP Optimizing Production and Logistics Processes
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems represents a significant advancement in optimizing production and logistics processes. This synergy leverages real-time data from connected devices to enhance the efficiency and responsiveness of core business functions. Understanding the individual components – IoT and ERP – and their combined potential is crucial to appreciating the transformative impact this integration offers.IoT, or the Internet of Things, refers to a network of physical objects—”things”—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet.
These “things” can range from simple sensors monitoring temperature to complex machinery providing real-time operational data. ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a system that integrates all facets of a business, including planning, purchasing inventory, sales, marketing, and human resources. It provides a centralized, integrated view of business operations, facilitating better decision-making and resource allocation.
Synergistic Potential of Integrating IoT in ERP Optimizing Production and Logistics Processes
The integration of IoT and ERP creates a powerful synergy. IoT devices generate a constant stream of real-time data regarding production processes, equipment performance, and inventory levels. This data is then fed into the ERP system, providing a dynamic and up-to-the-minute view of operations. This allows for proactive adjustments to production schedules, optimized resource allocation, and improved inventory management, all based on actual, real-time conditions rather than estimations or lagging indicators.
For example, a sensor detecting a malfunction in a machine on the factory floor can trigger an automated alert within the ERP system, prompting immediate maintenance scheduling and minimizing production downtime. This proactive approach, enabled by the integration, significantly reduces the risk of costly delays and production disruptions.
Key Benefits of Implementing IoT in ERP for Production and Logistics
Implementing IoT within an ERP system offers numerous benefits for production and logistics. These benefits translate directly into cost savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced responsiveness to market demands.The enhanced visibility provided by real-time data allows for better predictive maintenance. By analyzing sensor data from machines, potential failures can be identified before they occur, minimizing downtime and reducing the need for costly emergency repairs.
For example, a manufacturing plant might use IoT sensors to monitor vibration levels in its machinery. Anomalous vibration patterns detected by the sensors can trigger an alert in the ERP system, prompting preventative maintenance before a catastrophic failure occurs. This proactive approach significantly reduces unplanned downtime and associated costs.Further, real-time inventory tracking using IoT-enabled devices provides accurate and up-to-date information on stock levels.
This eliminates stockouts and minimizes the risk of overstocking, optimizing inventory management and reducing storage costs. Imagine a warehouse using RFID tags to track the movement of goods. The ERP system, integrated with this IoT network, provides a real-time view of inventory levels, enabling efficient order fulfillment and preventing stockouts. This enhanced visibility allows for optimized supply chain management, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced costs.Finally, improved traceability and quality control are significant benefits.
IoT sensors can monitor various parameters throughout the production process, ensuring that products meet quality standards and identifying potential defects early on. This reduces waste, improves product quality, and strengthens brand reputation. A food processing plant, for example, could use IoT sensors to monitor temperature and humidity throughout the production process. Any deviations from the pre-defined parameters would trigger an alert in the ERP system, enabling immediate corrective action and preventing spoiled products.
Optimizing Production Processes with IoT
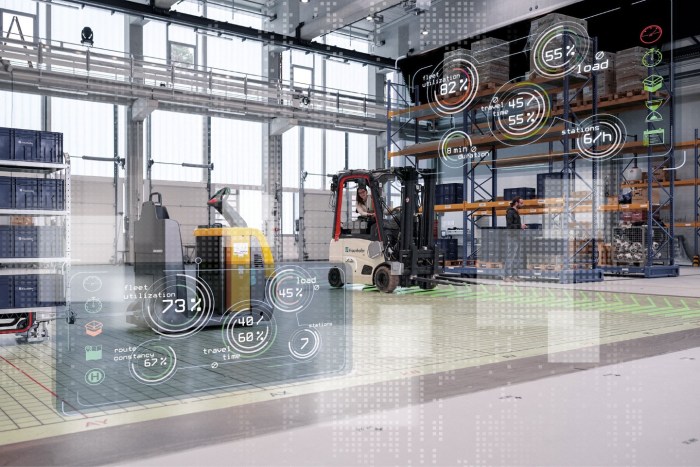

Integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technology into manufacturing processes offers significant opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. Real-time data collection and analysis, enabled by IoT sensors and devices, provide unparalleled insights into various aspects of the production line, leading to data-driven decision-making and optimized operations.Real-time Data and Production EfficiencyIoT sensors embedded within machinery and throughout the production environment collect a continuous stream of data, including machine performance metrics (speed, temperature, vibration), material flow, and product quality parameters.
This real-time data provides immediate visibility into the production process, allowing for rapid identification of inefficiencies and potential problems before they escalate. For example, a sudden increase in machine vibration might indicate impending equipment failure, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing costly downtime. Similarly, real-time monitoring of material flow can optimize inventory management and prevent production bottlenecks. This proactive approach, driven by real-time data, significantly improves overall production efficiency.
IoT Applications in Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance and quality control are two key areas where IoT significantly impacts manufacturing. Predictive maintenance leverages sensor data to anticipate equipment failures. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in sensor readings, manufacturers can schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing unexpected downtime and maximizing equipment lifespan. For example, a predictive maintenance system might alert operators to a potential bearing failure based on increased vibration levels, allowing for scheduled replacement before a catastrophic failure occurs.
Quality control benefits from IoT sensors that monitor product characteristics throughout the manufacturing process. Real-time data on dimensions, weight, and other quality parameters ensures consistent product quality and reduces defects. This leads to reduced waste, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced brand reputation.
Automating Production Processes and Reducing Downtime
IoT facilitates automation by connecting various production elements, including machines, robots, and human operators, through a unified network. This interconnectedness enables real-time communication and coordination, streamlining production workflows and reducing manual intervention. For example, an automated system can trigger a process adjustment based on real-time sensor data indicating a deviation from quality standards. Furthermore, the ability to remotely monitor and control equipment reduces downtime by allowing for quick identification and resolution of issues.
This proactive approach to maintenance and problem-solving minimizes production disruptions and maximizes overall efficiency.
Hypothetical Scenario: IoT Integration with ERP
Consider a hypothetical scenario where a manufacturing company integrates IoT sensors into its production line and connects the data to its Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system. Before IoT integration, the company experienced frequent unplanned downtime, high defect rates, and significant maintenance costs. After implementing IoT, real-time data provided early warnings of potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and process adjustments.
| Metric | Before IoT Integration | After IoT Integration | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Downtime (hours/month) | 150 | 50 | -66.7% |
| Production Output (units/month) | 10,000 | 12,000 | +20% |
| Defect Rate (%) | 5% | 2% | -60% |
| Maintenance Costs ($) | 50,000 | 30,000 | -40% |
Enhancing Logistics and Supply Chain Management
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems is revolutionizing logistics and supply chain management, offering unprecedented levels of visibility and control over the movement of goods. This enhanced visibility allows for proactive decision-making, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction. By leveraging real-time data from connected devices, businesses can optimize their entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery.IoT significantly enhances the tracking and monitoring of goods throughout the supply chain.
Real-time data from sensors and tracking devices embedded in products or packaging provides precise location information, enabling companies to monitor shipments at every stage of their journey. This granular visibility reduces uncertainties, minimizes delays, and allows for faster responses to potential issues. For instance, a refrigerated truck carrying perishable goods can be monitored for temperature fluctuations, allowing for immediate corrective action should the temperature deviate from the optimal range.
This proactive approach minimizes spoilage and ensures product quality.
IoT’s Role in Tracking and Monitoring Goods
Real-time tracking and monitoring capabilities provided by IoT offer significant benefits. Sensors on shipping containers can track location, temperature, humidity, and even shock levels. This data is transmitted wirelessly to a central system, providing a comprehensive view of the shipment’s status. This visibility extends beyond simple location tracking; it encompasses environmental conditions crucial for the integrity of the goods.
Predictive analytics can be applied to this data to anticipate potential delays or problems, enabling proactive interventions. For example, if a shipment is delayed due to unexpected traffic congestion, alternative routing can be implemented to minimize the impact on delivery timelines.
Improving Inventory Management and Reducing Stockouts
IoT devices such as RFID tags and barcode scanners provide real-time inventory data, enabling businesses to accurately track stock levels across the entire supply chain. This granular visibility minimizes the risk of stockouts by providing accurate forecasting capabilities. Furthermore, IoT-enabled automated inventory management systems can trigger automatic reordering when stock levels fall below a predefined threshold, ensuring continuous supply and preventing disruptions to production or sales.
Consider a retail company using IoT sensors to monitor shelf stock levels. When a particular item falls below a certain threshold, the system automatically places an order for replenishment, ensuring the product remains available for customers.
Challenges in Integrating IoT into Existing Logistics Systems and Proposed Solutions
Integrating IoT into existing logistics systems can present challenges, primarily concerning data integration, security, and interoperability. Many legacy systems lack the infrastructure to handle the volume and variety of data generated by IoT devices. Security concerns related to data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information also need to be addressed. Finally, the lack of standardization across different IoT devices and platforms can hinder interoperability.
To overcome these challenges, companies should invest in robust data integration platforms, implement strong cybersecurity measures, and adopt open standards for IoT devices and protocols. Investing in comprehensive training for staff to manage and interpret the data is also crucial.
Comparison of IoT Technologies Used in Supply Chain Optimization, IoT in ERP: Optimizing Production and Logistics Processes
Several IoT technologies are used for supply chain optimization, each with its strengths and weaknesses. RFID tags offer automatic identification and tracking of goods, while GPS tracking provides precise location information. Other technologies include Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons for indoor tracking and sensors for monitoring environmental conditions. RFID is particularly useful for tracking individual items within a larger shipment, offering a high level of granularity.
GPS tracking is more suitable for monitoring the location of larger shipments, such as entire truckloads. BLE beacons are useful for tracking assets within a warehouse or distribution center. The choice of technology depends on specific needs and requirements.
Best Practices for Securing IoT Devices in a Supply Chain Environment
Implementing robust security measures is paramount for protecting IoT devices and the sensitive data they generate. A multi-layered security approach is crucial.
- Employ strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to control access to IoT devices and data.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Implement data encryption to protect sensitive information transmitted between devices and the cloud.
- Utilize intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Establish a comprehensive security policy that Artikels procedures for managing and securing IoT devices.
- Regularly conduct security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential weaknesses.
Data Analysis and Decision Making: IoT In ERP Optimizing Production And Logistics Processes

The integration of IoT devices within an ERP system generates a vast amount of real-time data regarding production and logistics operations. This data, when effectively analyzed, provides invaluable insights for optimizing processes, improving efficiency, and ultimately boosting profitability. Harnessing this potential requires robust data analysis techniques and tools to transform raw data into actionable intelligence.The data collected from IoT sensors embedded in machinery, vehicles, and products provides a granular view of operations.
This includes information on machine performance (uptime, downtime, cycle times), product quality metrics (defect rates, yield), inventory levels, location of goods, and transportation times. This comprehensive data set empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions rather than relying on intuition or historical trends.
Data Visualization for Improved Understanding
Effective data visualization is crucial for interpreting the large volumes of data generated by IoT devices. Complex datasets become easily understandable when presented visually, allowing stakeholders to quickly identify trends, anomalies, and areas for improvement. Interactive dashboards, for example, can display key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, providing an immediate overview of operational performance. A typical dashboard might display metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), production throughput, inventory turnover rate, and on-time delivery percentage, all presented using charts and graphs.
For instance, a bar chart could compare the OEE of different production lines over a specific period, highlighting underperforming lines that require attention. A line graph could illustrate the trend of inventory levels over time, indicating potential stockouts or overstocking situations. A geographical map could show the location of shipments in real-time, facilitating proactive management of delivery schedules and addressing potential delays.
Predictive Analytics and Resource Allocation
Predictive analytics leverages historical IoT data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future events and optimize resource allocation. By analyzing patterns and trends in the data, businesses can anticipate potential problems, such as equipment failures or supply chain disruptions, before they occur. For example, by analyzing sensor data from a manufacturing machine, predictive models can identify anomalies indicating an impending failure.
This allows for proactive maintenance, preventing costly downtime and ensuring continuous production. Similarly, analyzing historical sales data and real-time inventory levels can predict future demand, enabling optimized inventory management and preventing stockouts or overstocking. Predictive analytics can also be used to optimize transportation routes, considering factors such as traffic conditions, weather patterns, and vehicle capacity to minimize delivery times and fuel consumption.
A real-world example is a logistics company using predictive analytics to anticipate potential delays due to inclement weather. By analyzing weather forecasts and historical data on delivery times during similar weather conditions, the company can proactively adjust delivery routes and schedules, minimizing disruptions and maintaining on-time delivery rates. This proactive approach prevents costly delays and enhances customer satisfaction.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
The successful integration of IoT into ERP systems is not merely a theoretical concept; it’s a reality shaping the efficiency and profitability of numerous organizations across various industries. Examining real-world applications provides invaluable insights into the tangible benefits and potential challenges of this technological convergence. The following case studies illustrate the diverse ways IoT enhances production and logistics processes.
Case Study 1: Improved Predictive Maintenance in a Manufacturing Plant
A major automotive manufacturer implemented an IoT-enabled predictive maintenance system. Sensors embedded within their assembly line machinery continuously monitored vibration, temperature, and pressure levels. This data was integrated with their ERP system, providing real-time insights into the health of each machine. The system’s predictive algorithms identified potential failures before they occurred, allowing for proactive maintenance scheduling. This significantly reduced downtime, minimized repair costs, and improved overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 15% within the first year.
The improved OEE translated to a substantial increase in production output and a reduction in production delays. The proactive maintenance approach also contributed to a safer working environment by preventing unexpected equipment failures.
Case Study 2: Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility in a Retail Distribution Network
A large retail company implemented IoT tracking devices on their shipping containers and pallets. This provided real-time location data, enabling them to monitor the movement of goods throughout their entire supply chain. Integration with their ERP system allowed for automated updates to inventory levels, improved order fulfillment accuracy, and reduced delivery times. The real-time visibility reduced instances of stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory management.
The system also facilitated proactive risk management by alerting stakeholders to potential delays or disruptions in the supply chain, allowing for timely interventions. The result was a 10% reduction in logistics costs and a 5% increase in on-time deliveries.
Case Study 3: Optimized Warehouse Operations through Automated Inventory Management
A leading e-commerce company deployed IoT-enabled sensors in their warehouses to monitor inventory levels, location, and environmental conditions (temperature, humidity). This data was fed into their ERP system, enabling automated inventory management and improved order picking efficiency. The system automatically alerted warehouse staff to low stock levels, ensuring timely replenishment. Real-time location tracking of goods within the warehouse streamlined the picking and packing process, leading to faster order fulfillment.
Furthermore, environmental monitoring ensured optimal storage conditions, minimizing product damage and spoilage. The company experienced a 20% increase in warehouse throughput and a 10% reduction in order fulfillment time.
Industry Expert Insights on Future Trends and Challenges
Industry experts predict that the convergence of IoT and ERP will continue to accelerate, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and edge computing. However, challenges remain, including data security concerns, the need for robust integration platforms, and the complexity of managing large volumes of IoT data. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a strategic approach that prioritizes data security, invests in scalable infrastructure, and fosters collaboration between IT and operational teams.
Furthermore, a strong focus on data analytics and the development of skilled workforce capable of interpreting and utilizing the insights generated by IoT-enabled ERP systems will be crucial for maximizing the benefits of this technology. Experts highlight the importance of selecting appropriate IoT devices and platforms that are compatible with existing ERP systems and can be seamlessly integrated.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Integrating IoT devices into ERP systems offers significant benefits, but it also introduces substantial security and privacy risks. The interconnected nature of these systems creates a larger attack surface, making robust security measures paramount to protect sensitive business data and maintain operational integrity. Failure to address these concerns can lead to data breaches, system disruptions, and significant financial losses.The increased number of access points inherent in IoT deployments significantly expands the potential vulnerabilities within an ERP system.
Malicious actors could exploit weaknesses in IoT devices, network infrastructure, or the ERP system itself to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, disrupt operations, or even inflict physical damage on equipment. This necessitates a multi-layered security approach encompassing device security, network security, and application security.
IoT Device Security
Securing individual IoT devices is crucial. This involves implementing strong authentication mechanisms, regularly updating firmware to patch vulnerabilities, and employing secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL to encrypt data transmitted between devices and the ERP system. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses in the devices themselves. Furthermore, choosing devices from reputable vendors with a proven track record of security is essential.
Devices should be equipped with robust access control mechanisms to limit who can interact with them and what actions they can perform.
Network Security
Protecting the network infrastructure connecting IoT devices to the ERP system is equally vital. This requires implementing robust firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and secure network segmentation to isolate IoT devices from other critical systems. Regular network monitoring and vulnerability scanning are necessary to identify and respond to potential threats promptly. Employing a virtual private network (VPN) for remote access to the system can further enhance security.
Proper network configuration, including the use of strong passwords and encryption protocols, is essential.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption is paramount to protect sensitive information transmitted and stored within the IoT-enabled ERP system. This includes encrypting data at rest and in transit using strong encryption algorithms. Implementing robust access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. Regular data backups and disaster recovery planning are essential to mitigate the impact of potential data breaches or system failures.
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools can be implemented to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the network unauthorized.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Adherence to data privacy regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), is critical. These regulations impose strict requirements on how personal and sensitive data is collected, processed, and stored. Organizations must implement appropriate data governance policies and procedures to ensure compliance. This includes conducting data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) to identify and mitigate potential risks, providing users with transparency about data collection practices, and implementing mechanisms for data subject access requests (DSARs).
Regular audits and assessments should be performed to verify ongoing compliance. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and reputational damage.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
The convergence of IoT and ERP is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in several key technologies. These advancements promise to further optimize production and logistics, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved decision-making. The next 5-10 years will see significant shifts in how businesses leverage this powerful combination.The integration of IoT and ERP is poised for significant expansion, fueled by innovations in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), edge computing, blockchain technology, and advanced analytics.
These technologies are not merely additive; they are fundamentally changing the nature of data collection, processing, and application within the manufacturing and supply chain environments.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing IoT-ERP Integration
Several emerging technologies are poised to significantly enhance the integration of IoT and ERP systems. These technologies will improve data quality, processing speed, and the overall analytical capabilities of the combined system.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source (the IoT devices) reduces latency and bandwidth requirements, enabling real-time analysis and faster responses to events on the factory floor or in the supply chain. This allows for immediate adjustments to production parameters or logistics routes based on real-time data analysis.
- Digital Twins: Virtual representations of physical assets (machines, products, etc.) provide a powerful tool for predictive maintenance, process optimization, and supply chain simulation. By analyzing data from the digital twin, businesses can identify potential issues before they occur, leading to reduced downtime and improved efficiency. For example, a digital twin of a production line could simulate the impact of changing parameters, allowing for optimization without disrupting the actual production process.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency and traceability by providing a secure and immutable record of product movement and provenance. This is particularly valuable in industries with stringent regulatory requirements or a need for high levels of accountability, such as pharmaceuticals or food production. For example, tracking the journey of a product from raw material sourcing to the final consumer, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting.
- Advanced Analytics and AI-powered Predictive Modeling: The combination of advanced analytics and AI-powered predictive modeling allows for more sophisticated analysis of IoT data, enabling proactive decision-making and improved forecasting. This can lead to better inventory management, optimized production scheduling, and more effective risk mitigation. For instance, predicting potential equipment failures based on sensor data and historical maintenance records, enabling preventative maintenance scheduling.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in IoT-Enabled ERP Systems
The integration of AI and ML into IoT-enabled ERP systems significantly enhances their capabilities. These technologies allow for automated decision-making, predictive analysis, and continuous optimization of production and logistics processes.AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of IoT data to identify patterns and anomalies that would be impossible for humans to detect manually. This enables proactive interventions, such as predictive maintenance, optimized resource allocation, and improved quality control.
For example, an AI-powered system could detect subtle variations in sensor data that indicate an impending equipment failure, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly downtime. Furthermore, ML models can learn and adapt over time, continuously improving their accuracy and effectiveness.
Evolution of IoT Applications in Production and Logistics
Over the next 5-10 years, we can expect a significant evolution in IoT applications within production and logistics. This evolution will be driven by the technological advancements discussed above, as well as the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and the growing demand for greater efficiency and transparency.We can anticipate a rise in autonomous systems, such as self-driving vehicles and robots, within logistics networks.
Production lines will become increasingly automated and interconnected, with real-time data analysis guiding production parameters and ensuring optimal performance. Supply chains will become more resilient and responsive, thanks to improved visibility and predictive analytics. For example, companies may use drones for inventory monitoring and delivery in remote locations, or implement AI-powered route optimization for efficient transportation of goods.
The integration of IoT and ERP will be instrumental in achieving these advancements.
The integration of IoT and ERP represents a significant leap forward in operational efficiency and strategic decision-making within the manufacturing and logistics sectors. By harnessing the power of real-time data and intelligent automation, businesses can optimize their processes, reduce costs, enhance responsiveness, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace. The future of industrial operations is undoubtedly intertwined with the continued evolution and wider adoption of IoT-enabled ERP systems, promising even greater levels of efficiency and innovation in the years to come.
FAQ Summary
What are the initial costs associated with implementing IoT in an ERP system?
Initial costs vary greatly depending on the scale of implementation, the existing IT infrastructure, and the specific IoT solutions chosen. Factors such as sensor deployment, software integration, and employee training all contribute to the overall expense. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial before undertaking any implementation.
How can data security be ensured with IoT devices connected to an ERP system?
Robust security measures are paramount. This includes employing strong encryption protocols, implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software and firmware, and establishing a comprehensive cybersecurity policy that addresses access control, data backups, and incident response procedures.
What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) commonly tracked using IoT data in ERP?
Common KPIs include production output, defect rates, machine downtime, inventory levels, order fulfillment times, supply chain lead times, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). The specific KPIs monitored will depend on the industry and business objectives.
What are the potential challenges in integrating IoT into legacy ERP systems?
Integrating IoT into older ERP systems can present challenges related to data compatibility, system scalability, and the need for extensive customization or system upgrades. Careful planning and a phased implementation approach can help mitigate these challenges.
READ MORE :
- https://rmm.abyadi.com/erp-and-internet-of-things-a-synergistic-future/
- https://rmm.abyadi.com/erp-and-iot-ecosystem-of-business/